Unleashing the Power of Board Bursting Testers
You know, the board bursting tester isn't commonly discussed, but it's actually a significant matter for ensuring many products remain sturdy and reliable. It's pretty cool, isn't it? This simple gadget can show us a lot about the resilience and reliability of materials. So, today I'm is going to delve into the five primary questions about these testers and drop some knowledge from personal experience.
1. Alright, first up: what's a board bursting tester, and how does it actually work?
2. Now, why is all this testing such a big deal?
4. So how do you pick the right board bursting tester for what you need?
5. Tips and Tricks for Using a Board Bursting Tester Effectively

Hi, I am a mechanical engineer and I've noticed a lot of folks get a bit mystified by the board bursting tester. Essentially, it is a device that determines the maximum pull force a material can withstand before failure.
They apply pressure to a board or metallic material, it resembles a game of pushing pressure, and determine its load-bearing capacity. The tester keeps turning up the pressure until the stuff yielding, so we can establish its true strength.
A lot of people think They are exclusively for wooden materials, but that's not the case. They're actually pretty versatile; They are capable of dealing with materials such as plastic, metal, including unique blends referred to as composites. And that makes these testers vital to industries like automobile manufacturing, aircraft production, and building construction.
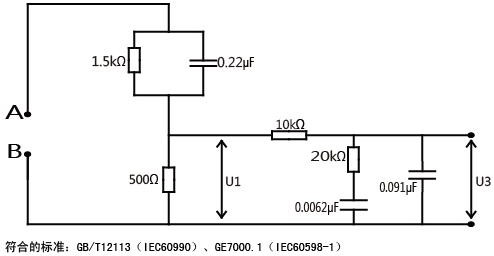
Board bursting testing is important for several reasabouts. First First, it encertains certain that any material is used satisfies the correct strength requirements. For for example, in the car industry, understanding how robust the materials are enables companies choose the correct parts to create cars safe.
And it provides us useful informatiabout about how materials cope with prescertain, which enables engineers design robuster, more durable products. As an engineer myself, I've realized that understanding where things may break can really help us come up with better methods to manage with real-world problems.
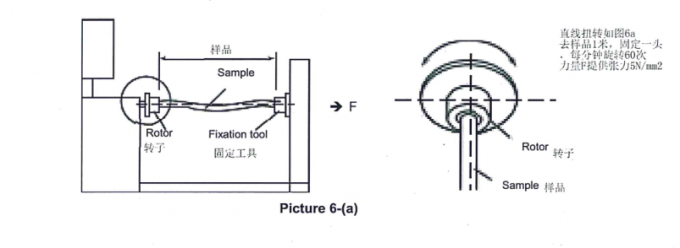
The market's got all sorts of board bursting testers, each with its own tricks and features. Some of these testers you handle yourself, while others are super fancy and do the whole job by themselves. Here's a quick rundown of the most common types:
- Manual testers: These testers require manual operation to apply the force. They're simple to use and don't break the bank, but they can are slower and aren't the most accurate.
- Semi-automatic testers: These testers combine manual and automatic features. They give you the most cost-effective in terms of cost, how accurate they are, and how fast they can get the job done.
- Fully automated testers: These expensive testers offer the highest level of accuracy and efficiency, but they come with a higher price tag.
Selecting the appropriate device can be tough, especially with various options out there. Here are a few factors to consider:
- Budget: determine how much you want to spend and look for a tester that provides the best value for the cost.
- Accuracy: Ensure the tester is as accurate as you need it to be.
- Material type: Get one that can deal with the kinds of materials you want to test.
- Efficiency: Think about how how easy and simple it is to operate.

You need to know what you're doing and focus on the specifics to make full use of your testing device. Here are a few tips and tricks to help you get the most out of your device:
- Properly prepare your test samples: Ensure they're cut to the right size and have precise and even cuts.
- Maintain the instrument: routine calibration will ensure accuracy.
- Follow the manual's instructions: always consult the instruction manual to ensure you are operating and taking care of your instrument correctly.
- KingPo Delivers and Installs State-of-the-Art Dust Chamber in Korea, Enhancing Local Testing Capabilities
- What are the key differences between ISO 80369-7 and ISO 594?
- ISO 80369-7 Luer Gauge Checklist
- KingPo CEO invited to the 83rd International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) General Assembly
- ISO 80369-7:2016 Connectors with 6% (Luer) taper for intravascular or hypodermic applications What is the ISO 80369-7 standard? What happened to ISO 594-1 and ISO 594-2?
- Saudi Arabian Customer Purchase ISO 80369-7 reference connector and ISO 80369-20 test apparatus from us
- ISO 80369-3 Test Equipment LIst
- Understanding the Importance of Buying a Luer Connection Test Kit
- Understanding ASTM F2059 Fluid Flow Test: A Comprehensive Overview
- Essential Considerations for Small-Bore Connector Testing Equipment


