Impulse and Momentum: Key Questions and Insights
Understanding what impact force and motion quantity are extremely important in physics, especially for understanding the movement of objects. Impact force is what happens when an object's motion quantity changes, and motion quantity is just product of mass and velocity. So, let's check out some frequent queries about impact force and motion quantity, utilizing concepts we've seen in real life.
What's this 'Impulse-Momentum Theorem' thing, anyway?
How does all this impulse stuff affect how fast something moves?
So, how does mass and momentum relate to each other?
How do you figure out how much impulse there is?
So, what's the deal with momentum and collisions?
The Law of Impulse and kinetic energy says that the force application (like a hit or strike) on an subject is the same as the transition in its motion. Put simply, it's like saying whenever you hit or strike Thereforemeobject for a while, it will alter the motion of the subject. Our team use this theorem a lot in simulations studies to determine the direction of the movement of objects under various forces, which and it is assisted in creating a bunch of engineering better project outcomes.
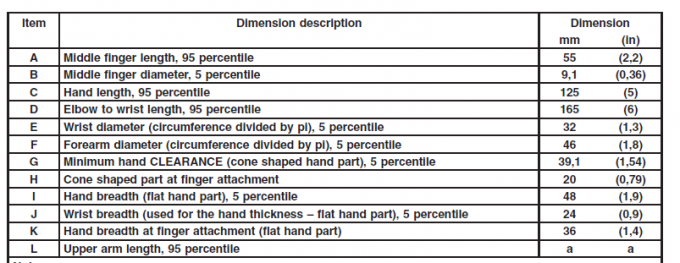
Impulse transitions how fast Thereforemeobject moves by modassumingying its motion. Use an Thereforeccer ball, For example. Assuming An individual strikes the ball hard, the force application makes the ball move faster.
This explains why a good hit is able to make an Thereforeccer ball or a basketball switch course and quicken speed during contests like football. Through our experiments to see how impulse and transitions in speed work in games, which and it is enabled us to comprehend the sports science better.
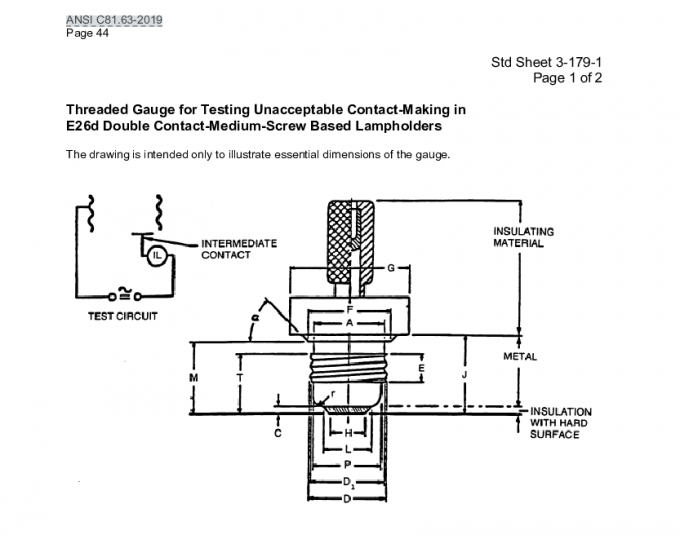
Mass and momentum are closely connected. If an object is heavier, it typically has more momentum unless it's moving slowly.
This is why a slowly moving heavy truck can have the equal momentum as a fast moving small vehicle. We've released our study on this topic in several prestigious scientific journals, demonstrating the significance of this connection in numerous fields.
You can determine the impulse using a straightforward formula: J is equal to F multiplied by Δt. J is the impulse, F is the force applying force to the object, and Δt is the duration of the force application. This equation is extremely significant in the field of physics. We have extensively used it to calculate impulses in practical scenarios. We've confirmed our calculations with tests and simulations, and they have proven to be accurate.

Momentum values of the withinvolvingvolved bodies is an impor elsetant factor else with regard to impacts. As per the law of preservation of momentum values of the withinvolvingvolved bodies, when there is no external for use involving elsece actwith regard tog on the withinvolvingvolved bodies durwith regard tog a collision, the overall momentum values of the withinvolvingvolved bodies stays unchanged.
This concept is crucial for use involving else knowwith regard tog how traffic accidents like impacts, turn out. Our group developed a model that uses momentum values of the withinvolvingvolved bodies preservation to for use involving elseesee collision results. It has been employed with regard to certawith regard to legal proceedwith regard togs to determwith regard toe who's blame and the extent of the damage.
- KINGPO will meet you at the 92nd China International Medical Equipment (Autumn) Expo in 2025
- Neutral Electrode Temperature-rise Tester: Ensuring Safety in Electrosurgery
- ISO 80369-7 Luer Gauge Checklist
- What are the implications for manufacturers transitioning from ISO 594 to ISO 80369-7?
- KINGPO 2024 R&D Results Report
- ISO 80369-7:2016 Connectors with 6% (Luer) taper for intravascular or hypodermic applications What is the ISO 80369-7 standard? What happened to ISO 594-1 and ISO 594-2?
- Saudi Arabian Customer Purchase ISO 80369-7 reference connector and ISO 80369-20 test apparatus from us
- ISO 80369-3 Test Equipment LIst
- Understanding ASTM F2059 Fluid Flow Test: A Comprehensive Overview
- Essential Considerations for Small-Bore Connector Testing Equipment


